Introduction to the column design as per ACI 318 code
Column design is the most important part of reinforced concrete structures of residential, commercial, or industrial buildings. Columns should be designed properly as they are the most important part of structures to support and transfer loads from structures to foundations.
To learn about column design visit qLearnify
What is a column?
The column is a structural member that transfers load from the beam and slab through its axis. Different types of columns are available. They are commonly used in buildings, bridges, and other structures to ensure stability and support.
Common cross-sectional shapes include rectangular, square, circular, or L-shaped. Specialized designs may feature T-shaped, I-shaped, or polygonal columns.
Types of Columns as per Loads:
- Axially Loaded Columns – only carry gravity loads without many moments.
- Biaxial Columns – Carry axial load as well as a moment from both directions.
- Lateral Load Columns – Carry axial load as well as the moment and lateral load from earthquake and wind load.
Types of Columns as per materials:
- Reinforced Concrete – column constructed with concrete for strength and durability.
- Steel – PEB steel section used to build high-strength structures for building.
- Timber – column used for architectural purposes.
- Composite Materials – Columns created using composite materials like steel, concrete, timber, etc.
Design Principles According to ACI 318 Code
To design a column, a structural engineer follows different types of rules for strength and stability. There are many structural design codes available as follows for design and analysis.
Structural Engineering Codes
- ACI 318: Building Code Requirements for Structural Concrete (USA)
- Eurocode 2 (EN 1992): Design of Concrete Structures (Europe)
- BS 8110: Structural Use of Concrete (UK)
- IS 456: Code of Practice for Plain and Reinforced Concrete (India)
- AS 3600: Concrete Structures (Australia)
Steel Design Codes
- AISC 360: Steel Construction Manual (USA)
- Eurocode 3 (EN 1993): Design of Steel Structures (Europe)
- BS 5950: Structural Use of Steelwork in Building (UK)
- IS 800: General Construction in Steel (India)
- AS 4100: Steel Structures (Australia)
Important parameters
Materials Properties
Concrete Unit Weight (MKS)
- Stone Aggregate (unreinforced)=22.8 KN/𝑚^3
- Brick Aggregate (unreinforced)=20.4 KN/𝑚^3
for reinforced concrete, add 0.63 KN/m3 for each 1% by volume of main reinforcement
Concrete Unit Weight (FPS)
- Stone Aggregate- 150 lb/cft
- Brick Aggregate- 135 lb/cft
Modulus Of Elasticity (MKS)
- Stone Aggregate =4700x√(𝑓′𝑐) (𝑀𝑃𝑎)
- Brick Aggregate=3750x√(𝑓′𝑐) (𝑀𝑃𝑎)
Modulus Of Elasticity (FPS)
- Stone Aggregate =57000x√(𝑓′𝑐) (𝑝𝑠𝑖)
- Brick Aggregate =45155x√(𝑓′𝑐) (𝑝𝑠𝑖)
Note:
- Unless otherwise specified, f’c shall be based on 28-day tests.
- Minimum concrete strength = 20 MPa but up to 4 storeys 17MPa may be relaxed.
The design strength of reinforcement
- The design strength of reinforcement represented by the values of 𝑓𝑦 used in design calculations shall not exceed 550 MPa.
- for transverse reinforcement, 𝑓𝑦t may exceed 420 MPa.
- Modulus of elasticity, 𝐸𝑠, for reinforcement, shall be permitted to be taken as 200,000 MPa.
Strength reduction factor (𝜙) For compression-controlled sections
- Members with spiral reinforcement conforming – 0.75
- Other reinforced members – 0.65
Column Design Rule
Compression Members Reinforcement Limitation
The area of longitudinal reinforcement, 𝐴𝑠𝑡, shall be not less than 0.01𝐴𝑔 or more than 0.06𝐴𝑔.
The ACI Code specifies a minimum number of longitudinal bars in compression members shall be,
- 4 for bars within rectangular or circular ties
- 3 for bars within triangular ties
- 6 for bars enclosed by spirals conforming
Moment of Inertia (𝐼)
The moment of inertia for columns is calculated as 𝐼 = 0.70𝐼𝑔, where 𝐼𝑔 is the moment of inertia of the gross cross-section of the column.
Clear Distance Between Longitudinal Bars
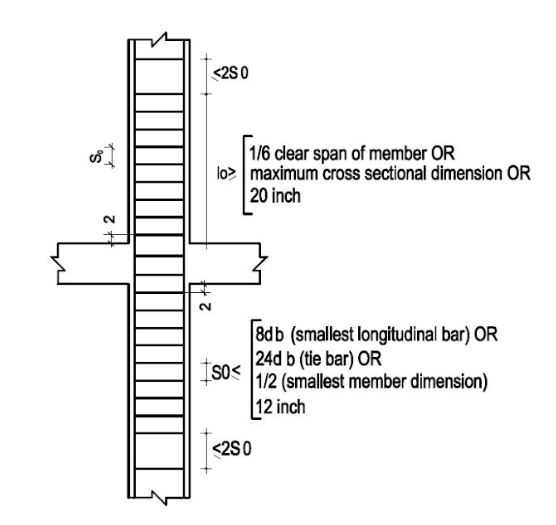
For compression members, the clear distance between longitudinal bars shall be not less than
- 1.5 bar diameters
- 40 mm (1.5in)
- 1.33 times the maximum nominal size of coarse aggregate.
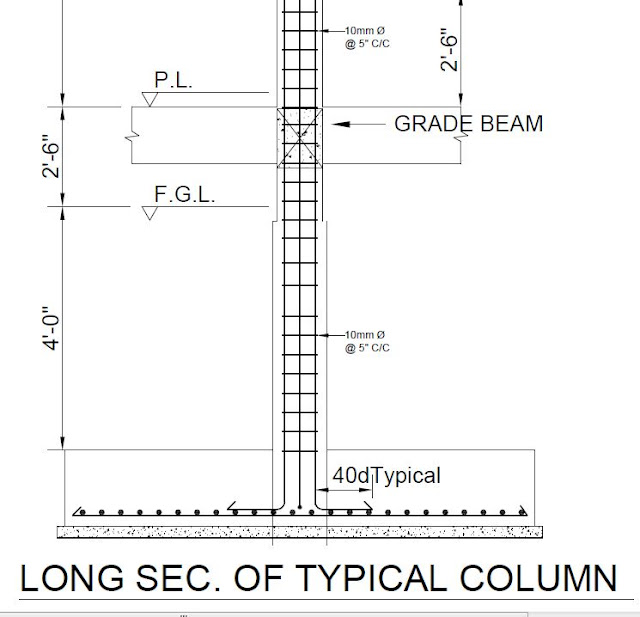
The minimum cross-sectional dimension for a Column: is 9″x 12″ (225 MM x 300 MM) which is the minimum recommended size.
Required Reinforcement for a Column: minimum 1% and maximum 6% of the sectional area of the column.